
[ad_1]
Processing And Studying From Video
I lately learn a web based article suggesting that movies are finest for instructing. The article stated (flippantly edited for anonymity, as I might reasonably not embarrass anybody): “We all know from analysis that movies make processing and reminiscence recall extra environment friendly. They attraction to a large viewers and permit every consumer to course of info in the best way that’s finest for them. No surprise video is finest for instructing!”
I’ve seen related—and often far too simplistic—feedback. Video is an efficient software for some tutorial functions, and fewer so for others. And even when video is an efficient software, it’s far much less so when it isn’t designed nicely. The edited quote implies that movies are good as a result of they attraction to totally different studying kinds, and though the educational kinds fantasy has clearly been debunked (Pashler, 2008), this fantasy has achieved zombie standing, and refuses to die. In Half 1 of my sequence on video and studying, I mentioned selecting media and instruments reminiscent of video for digital instruction. Among the essential factors I made embody:
- The aim of this sequence of evidence-informed articles is to reply the query, “how ought to we create tutorial movies to raised foster studying?”
- Though some analysis typically reveals constructive results for video on studying, different analysis reveals movies too typically aren’t watched or are solely partially watched.
- The easiest way to pick out digital instruments and applied sciences is to match essential instructing and studying actions to the instruments that finest help them. Video doesn’t help all essential instructing and studying actions so many (most) instances, we want multiple software.
- Content material and social interactions are sometimes finest supported by very totally different instruments. Analysis factors to the necessity for each content material and social interactions, so once more, we want multiple software.
- Whereas video has many strengths (reminiscent of the flexibility to cease, begin, and evaluation), it additionally has challenges (reminiscent of the flexibility for us to seemingly watch it with out processing the content material).
In Half 2 (this text), I’ll talk about how people course of video and the implications for designing it so we will be taught from it. Though there may be analysis exhibiting video will help studying, poorly designed video could make studying more durable, and we should keep away from these poor designs! I’ll begin by discussing how we course of multimedia, particularly video, and what can go improper in poorly designed video instruction. Then I’ll talk about what analysis tells us about making video higher for psychological processing. Since higher processing of video is vital to remembering, understanding, and use, realizing what we have to do is really a giant deal!
Processing Video For Studying
Multimedia, reminiscent of video, is outlined as static or transferring photographs plus auditory info introduced concurrently. Combining media sorts to create info or instruction—reminiscent of textual content, static photographs reminiscent of pictures and drawings, transferring photographs reminiscent of video and animations, and audio—are widespread types of multimedia. Educational displays exhibiting static or transferring photographs and auditory info concurrently is known as multimedia studying (Mayer, 1997; 2001).
Mayer’s (2005) cognitive principle of multimedia studying (CTML) tells us how we course of and be taught from multimedia instruction. CTML is constructed on three assumptions: dual-channel, restricted capability, and energetic processing (Mayer, 2005).
- Twin-channel assumption
The twin-channel assumption tells us there are two separate channels—visible and auditory—that course of info in working reminiscence. The visible channel processes static and transferring photographs in addition to written phrases. The auditory channel processes narrations and different sounds. - Restricted capability assumption
The restricted capability assumption explains that every channel has a restricted capability to course of info at any given second. Studying is hindered or stopped when limits are exceeded. - Lively processing assumption
The energetic processing assumption tells us that to be taught, contributors should actively course of what they’re watching and listening to (Mayer, 2005; 2009). Video could look like passive as a result of we don’t see folks mentally processing. But when they’re actively mentally processing (making sense of the content material, organizing it, integrating it with prior data) it isn’t passive.
Working reminiscence is the place visible and auditory processing happens, however it is vitally restricted in quantity and period. Lengthy-term reminiscence is the place info is saved for long-term retrieval and use, however the means of getting info into long-term storage is just not easy. I talk about the method from seeing and listening to to processing to storing in my webinar, which you’ll be able to watch free of charge.
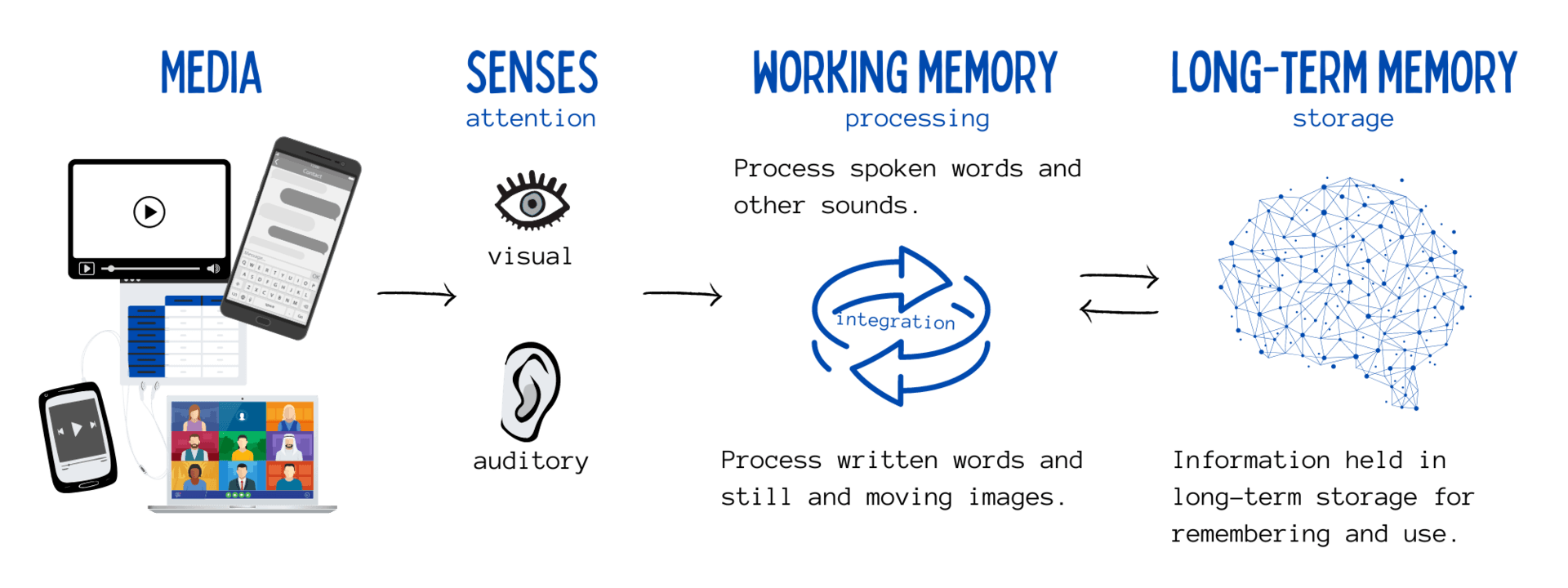
Picture 1: Patti Shank’s webinar recording
When contributors aren’t processing the video or aren’t watching the video, they can not be taught from it. And sadly, analysis reveals that that is commonplace. Guo and colleagues (2014) researched participant video viewing in 4 edX MOOCs, analyzing seven million video-watching classes. When contributors watched movies lower than six minutes lengthy, they watched the entire video. As movies lengthened, contributors watched much less and fewer. For instance, the median watching time dropped to close 50% for 9–12-minute movies, and to about 20% for over 12-minute movies (Guo et al., 2014).
Video can improve studying as a result of processing with two channels can scale back cognitive load and assist watchers combine related visible and auditory info. These of us who construct multimedia studying reminiscent of video can even assist contributors handle cognitive load, by modifying the video to take out pointless sources of psychological effort and add in results that enhance consideration and understanding. For instance, we will edit out pointless info and add annotations to cue contributors to vital components of the video. And contributors themselves can handle cognitive load by stopping, beginning, pausing, and reviewing the video. These consumer controls are extraordinarily advantageous for studying from video (Tallent-Runnels, 2006).
Video not designed nicely could make it more durable to adequately give attention to or course of video content material (Costley and Lange, 2017; Mayer, 2014). We should subsequently design video in alignment with how we course of multimedia. Mayer (2014; 2020) launched a sequence of multimedia studying ideas to assist us higher design multimedia in three classes of learner processing: extraneous processing, important processing, and generative processing. Extraneous processing damages studying and must be averted. Important processing is brought on by the complexity of the supplies and must be managed. And germane psychological processing helps us extra deeply perceive and must be inspired.
Multimedia Design Rules
The precise sorts of psychological processing are vital to studying. Mayer’s (2020) multimedia studying design ideas are categorized into three kinds of psychological processing: extraneous processing (dangerous), important processing (wanted), and generative processing (very useful). These ideas are used to keep away from extraneous processing, handle important processing, and enhance germane processing throughout instruction.
The data within the subsequent three sections is tailored from Mayer’s third version of Multimedia Studying (2020). On this ebook, he cites the big variety of analysis on which his ideas are primarily based and the primary situations for these ideas. If you need this extra info, I extremely suggest getting the ebook.
1. Keep away from Extraneous Processing
Extraneous psychological processing wastes our restricted processing means and doesn’t help with assembly tutorial targets. It leaves much less psychological effort accessible for important and germane processing, which assist studying. Listed here are 5 multimedia ideas that assist keep away from extraneous processing.
- Coherence precept
The coherence precept says we be taught finest from multimedia after we embody concise, vital materials, and do not embody expanded, much less vital materials. This implies we should always typically keep away from attention-grabbing however irrelevant particulars and supplies which are distracting and never wanted (reminiscent of background music). When pointless auditory info is added, for instance, it competes with the narration for processing within the auditory channel. This implies much less capability for taking note of narration. - Signaling precept
The signaling precept says we be taught finest from multimedia after we add visible cues (e.g., an arrow) or auditory cues (e.g., a narrated sentence about what we’re about to debate) highlighting the group of vital materials. Signaling reduces the necessity to attempt to determine what’s vital and what’s much less so. - Redundancy precept
The redundancy precept says we be taught finest from multimedia when utilizing photographs and narration reasonably than photographs, narration, and printed textual content, particularly when the lesson is quick paced. When narration explains photographs, folks would not have to make use of further psychological effort to travel between the pictures and the printed textual content. - Spatial contiguity precept
The spatial contiguity precept says we be taught finest from multimedia when corresponding phrases and pictures are bodily shut collectively. When corresponding phrases and photos are shut, folks would not have to make use of further psychological effort to look the web page or display to see what goes collectively. - Temporal contiguity precept
The temporal contiguity precept says we be taught finest from multimedia when narration and pictures play on the similar time, reasonably than one after one other. When corresponding narration and pictures are introduced on the similar time, persons are higher in a position to make psychological connections between them.
An instance of making use of the spatial contiguity precept is proven under. The highest illustration of clarinet components requires you to match the numbers with the half names under, including pointless psychological effort. The spatial contiguity precept has been utilized to the underside illustration to make it simpler to view the identify of every piece with out having to match them up.
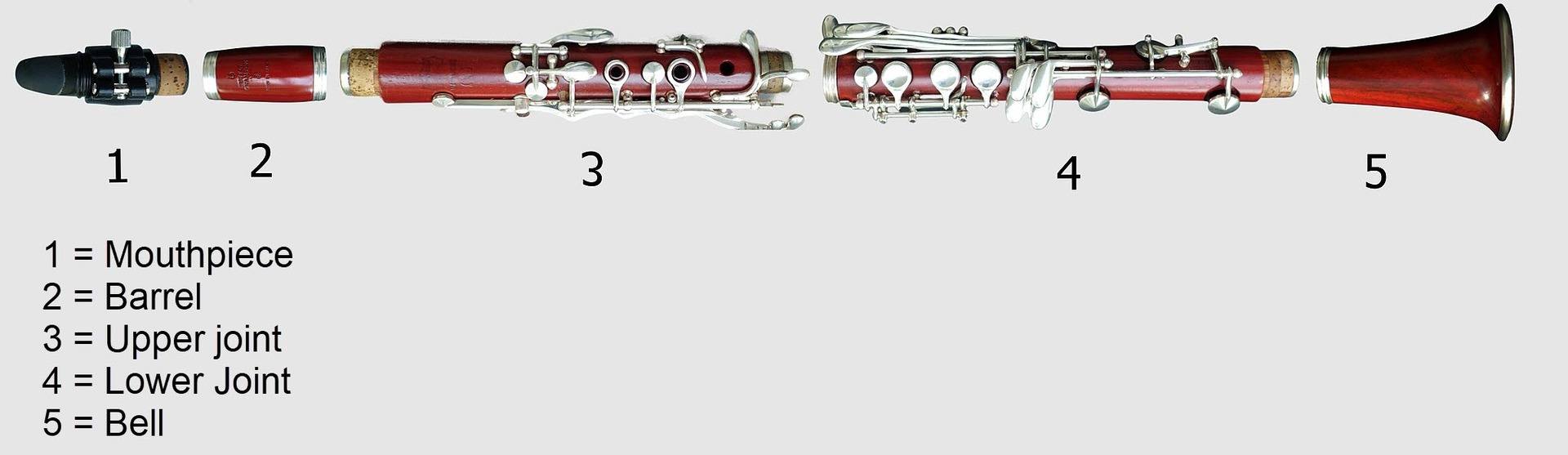


Picture 2: Wikimedia Commons (Gisbert König, CC0), tailored by Patti Shank
2. Handle Important Processing
Important processing is the psychological processing wanted to take care of the complexity of the supplies whereas within the working reminiscence. Important processing is subsequently wanted to be taught. Listed here are three multimedia ideas that assist handle important processing.
- Segmenting precept
The segmenting precept says that we be taught finest from multimedia when it’s introduced in user-paced segments. Because of this studying supplies must be chunked into smaller, coherent sections, and contributors ought to have the ability to management playback, particularly when the fabric is advanced and quick paced. It will assist folks course of the fabric they’re at the moment watching/listening to earlier than transferring on. - Pretraining precept
The pretraining precept says that we be taught finest from multimedia after we know the names (phrases, definitions) and traits of essential ideas first. Pretraining will help handle important processing, by working by pretraining components earlier than principal classes. - Modality precept
The modality precept says that we be taught finest from multimedia when utilizing photographs and spoken phrases reasonably than photographs and printed phrases. Pictures and spoken phrases use each channels (visible and auditory) as an alternative of only one. In a narrated presentation, spoken phrases are processed by the auditory channel, permitting more practical processing of photographs within the visible channel.
3. Encourage Germane Processing
Germane processing is the psychological processing wanted to deeply perceive and is expounded to the quantity of effort the participant is keen to expend. These 4 multimedia ideas are supposed to encourage germane processing.
- Personalization precept
The personalization precept says we be taught finest from multimedia after we use a conversational fashion, reasonably than a extra educational or formal fashion. When folks really feel that we’re speaking to them, they’re extra prone to put effort into making sense of what’s being stated. - Voice precept
The voice precept says that we be taught finest from multimedia when the narration is spoken in a nice, human voice, reasonably than in a machine voice. When folks really feel that we’re speaking to them, they’re extra prone to put effort into making sense of what’s being stated. - Embodiment precept
The embodiment precept says that we be taught finest from multimedia when an on-screen teacher makes use of social gestures, physique actions, and facial/eye expressions whereas explaining. When folks see these cues, they’re extra prone to put effort into making sense of them. - Generative exercise precept
The generative exercise precept says we be taught finest from multimedia after we are concerned in studying actions reminiscent of summarizing, imagining, self-testing, self-explaining, instructing, or enacting whereas studying. These actions enhance psychological processing throughout studying and assist folks combine new studying with related prior data from long-term reminiscence.
If the ideas for germane processing look totally different than you bear in mind, Mayer made some evidence-informed adjustments in his newest model of Multimedia Studying (2020).
Received It?
The data on this article is advanced, so let’s use some multiple-choice questions to recollect key factors. Solutions are on the finish of the article.
Q1. What’s multimedia studying?
a) Using static or transferring photographs, plus auditory info, which are used on the similar time
b) Simultaneous static or transferring photographs and auditory info utilized in tutorial messages
c) Transferring photographs (reminiscent of video or animation) used to ship participating info or instruction
Q2. What does the dual-channel assumption inform us?
a) Now we have two separate channels in sensory reminiscence to course of info: visible and auditory
b) Now we have two separate channels in long-term reminiscence to course of info: visible and auditory
c) Now we have two separate channels in working reminiscence to course of info: visible and auditory
Q3. Underneath which of those situations are we utilizing each channels without delay?
a) Video with simultaneous narration
b) Animation with written textual content
c) A static picture with written textual content
This fall. The restricted capability assumption tells us that:
a) We are able to course of extra after we use just one channel at a time
b) We’re unable to course of multiple visible object at a time
c) Every channel has a restricted capability to course of info
Q5. The cognitive principle of multimedia studying (CTML) says we have to design multimedia reminiscent of video in accordance with which assumptions about how our minds course of multimedia?
a) Extraneous, important, and germane processing
b) Twin-channel, restricted capability, and energetic processing
c) Sensory, working, and long-term processing
Q6. Studying requires which kind of effort to retailer what we’ve discovered for later use?
a) Bodily effort
b) Psychological effort
c) Each bodily and psychological effort
Q7. The place can we retailer what now we have discovered, so we will use it later?
a) Lengthy-term reminiscence
b) Working reminiscence
c) Sensory reminiscence
Q8. Do Mayer’s multimedia design ideas inform us it’s higher to have concise and solely related studying supplies, or to additionally embody added and expanded content material?
a) Added and expanded
b) Concise and related
c) Is dependent upon participant age
Q9. Do Mayer’s multimedia design ideas inform us it’s higher to make use of narration to explain visuals or to make use of written textual content to explain visuals?
a) Narration ought to describe visuals
b) Written textual content ought to describe visuals
c) Narration or textual content can describe visuals
Q10. Designers and instructors ought to decrease which kind of psychological processing?
a) Important
b) Germane
c) Extraneous
Subsequent Time
This text mentioned essential insights about how we course of multimedia, together with video. Mayer’s ideas for designing multimedia/video have been introduced so we all know the perfect methods to course of multimedia studying successfully. Within the subsequent article, we’ll particularly talk about utility of design in accordance with how folks course of video.
Appropriate Solutions:
1(b), 2(c), 3(a), 4(c), 5(b), 6(b), 7(a), 8(b), 9(a), 10(c)
References:
- Brame, C. J. 2016. “Efficient academic movies: Rules and pointers for maximizing scholar studying from video content material.” CBE Life Sciences Training 15 (4): 1–6.
- Çeken, B., and N. Taşkın. 2022. “Multimedia studying ideas in numerous studying environments: A scientific evaluation.” Good Studying Environments 9 (19).
- Costley, J., and C. H. Lange. 2017. “Video lectures in e-learning: Results of viewership and media variety on studying, satisfaction, engagement, curiosity, and future behavioral intention.” Interactive Expertise and Good Training 14 (1): 14–30.
- Guo, P. J., J. Kim, and R. Robin. 2014. “How video manufacturing impacts scholar engagement: An empirical research of MOOC movies.” [email protected] ’14 Proceedings of the First ACM Convention on Studying at Scale. New York: ACM, 41–50.
- Ibrahim, M. 2012. “Implications of designing tutorial video utilizing Cognitive Concept of Multimedia Studying.” Important Questions in Training 3 (2): 83–104.
- Lange, C., and J. Costley. 2020. “Enhancing on-line video lectures: Studying challenges created by media.” Worldwide Journal of Instructional Expertise in Greater Training 17 (16).
- Mayer, R. E. 1997. “Multimedia studying: Are we asking the fitting questions?” Instructional Psychologist 32 (1): 1–19.
- Mayer, R. E. 2001. Multimedia Studying. New York: Cambridge College Press.
- Mayer, R. E. 2005. “Cognitive Concept of Multimedia Studying.” In The Cambridge Handbook of Multimedia Studying, edited by R. E. Mayer. New York: Cambridge College Press, 31–48.
- Mayer, R. E. 2009. Multimedia Studying. 2nd Version. New York: Cambridge College Press.
- Mayer, R. E. 2014. “Cognitive Concept of Multimedia Studying.” In The Cambridge Handbook of Multimedia Studying, edited by R. E. Mayer. New York: Cambridge College Press, 43–71.
- Mayer, R. E. 2020. Multimedia Studying. third Version. New York: Cambridge College Press.
- Mayer, R. E., and R. Moreno. 2000. “A Coherence Impact in Multimedia Studying: The Case for Minimizing Irrelevant Sounds within the Design of Multimedia Educational Messages.” Journal of Instructional Psychology 92 (1): 117–125.
- Mayer, R. E., and R. Moreno. 2003. “9 methods to scale back cognitive load in multimedia studying.” Instructional Psychologist 38 (1): 43–52.
- Paivio, A. 1971. Imagery and Verbal Processes. New York: Holt, Rinehart and Winston.
- Paivio, A. 1986. Psychological Representations: A Twin Coding Strategy. New York: Oxford College Press.
- Pashler, H., M. McDaniel, D. Rohrer, and R. Bjork. 2008. “Studying kinds: Ideas and Proof.” Psychological Science within the Public Curiosity 9 (3): 105–119.
- Risko, E. F., N. Anderson, A. Sarwal, M. Engelhardt, and A. Kingstone. 2012. “On a regular basis consideration: variation in thoughts wandering and reminiscence in a lecture.” Utilized Cognitive Psychology 26: 234–242.
- Rudolph, M. 2017. “Cognitive principle of multimedia studying.” Journal of On-line Greater Training 1 (2).
- Shank, P. 2018. Ought to We Use Background Music With Instruction? No.
- Shank, P. 2022. Creating Higher Video For Studying, Half 1
- Sweller, J. 1989. “Cognitive know-how: Some procedures for facilitating studying and problem-solving in arithmetic and science.” British Journal of Instructional Psychology 81 (4): 457–466.
- Sweller, J. 1994. “Cognitive load principle, studying issue, and tutorial design.” Studying and Instruction 4 (4): 295–312.
- Sweller, J., J. J. G. van Merriënboer, and F. Paas. 1998. “Cognitive structure and tutorial design.” Instructional Psychology Evaluation 10: 251–296.
- Tallent-Runnels, M. Okay., J. A. Thomas, W. Y. Lan, S. Cooper, T. C. Ahern, S. M. Shaw, and X. Liu. 2006. “Instructing programs on-line: A evaluation of the analysis.” Evaluation of Instructional Analysis 76 (1): 93–135.
[ad_2]